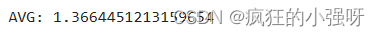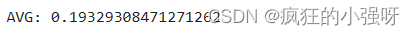数据挖掘入门项目二手交易车价格预测之建模调参
文章目录
- 目标
- 步骤
- 1. 调整数据类型,减少数据在内存中占用的空间
- 2. 使用线性回归来简单建模
- 3. 五折交叉验证
- 4. 模拟真实业务情况
- 5. 绘制学习率曲线与验证曲线
- 6. 嵌入式特征选择
- 6. 非线性模型
- 7. 模型调参
- (1) 贪心调参
- (2)Grid Search 调参
- (3)贝叶斯调参
- 总结
本文数据集来自阿里天池:https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/231784/information
主要参考了Datawhale的整个操作流程:https://tianchi.aliyun.com/notebook/95460
小编也是第一次接触数据挖掘,所以先跟着Datawhale写的教程操作了一遍,不懂的地方加了一点点自己的理解,感谢Datawhale!
目标
了解常用的机器学习模型,并掌握机器学习模型的建模与调参流程
步骤
1. 调整数据类型,减少数据在内存中占用的空间
具体方法定义如下:
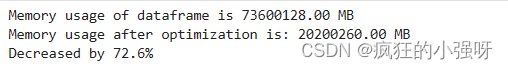
对每一列循环,将每一列的转化为对应的数据类型,在不损失数据的情况下,尽可能地减少DataFrame中每列的内存占用
def reduce_mem_usage(df): """ iterate through all the columns of a dataframe and modify the data type to reduce memory usage. """ start_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() # memory_usage() 方法返回每一列的内存使用情况,sum() 将它们相加。 print('Memory usage of dataframe is {:.2f} MB'.format(start_mem)) # 对每一列循环 for col in df.columns: col_type = df[col].dtype # 获取列类型 if col_type != object: # 获取当前列的最小值和最大值 c_min = df[col].min() c_max = df[col].max() if str(col_type)[:3] == 'int': # np.int8 是 NumPy 中表示 8 位整数的数据类型。 # np.iinfo(np.int8) 返回一个描述 np.int8 数据类型的信息对象。 # .min 是该信息对象的一个属性,用于获取该数据类型的最小值。 if c_min > np.iinfo(np.int8).min and c_max np.iinfo(np.int16).min and c_max np.iinfo(np.int32).min and c_max np.iinfo(np.int64).min and c_max np.finfo(np.float16).min and c_max np.finfo(np.float32).min and c_max调用上述函数查看效果:
其中,data_for_tree.csv保存的是我们在特征工程步骤中简单处理过的特征
sample_feature = reduce_mem_usage(pd.read_csv('data_for_tree.csv'))2. 使用线性回归来简单建模
因为上述特征当时是为树模型分析保存的,所以没有对空值进行处理,这里简单处理一下
sample_feature.head()
可以看到notRepairedDamage这一列有异常值‘-’:
sample_feature = sample_feature.dropna().replace('-', 0).reset_index(drop=True) sample_feature['notRepairedDamage'] = sample_feature['notRepairedDamage'].astype(np.float32)建立训练数据和标签:
train_X = sample_feature.drop('price',axis=1) train_y = sample_feature['price']简单建模:
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression model = LinearRegression() model = model.fit(train_X, train_y) 'intercept:'+ str(model.intercept_) # 这一行代码用于输出模型的截距(即常数项) sorted(dict(zip(sample_feature.columns, model.coef_)).items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True) # 这行代码是用于输出模型的系数,并按照系数的大小进行排序 # sample_feature.columns 是特征的列名。 # model.coef_ 是线性回归模型的系数。 # zip(sample_feature.columns, model.coef_) 将特征列名与对应的系数打包成元组。 # dict(...) 将打包好的元组转换为字典。 # sorted(..., key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True) 对字典按照值(系数)进行降序排序。
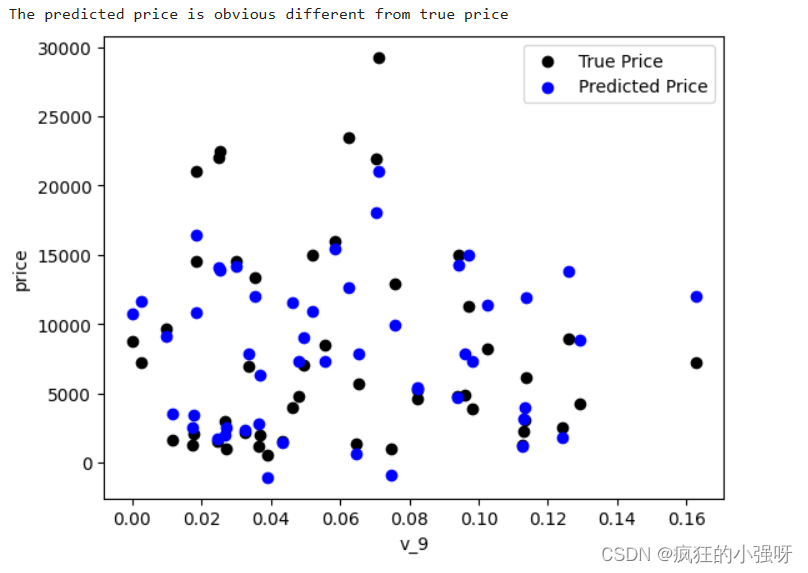
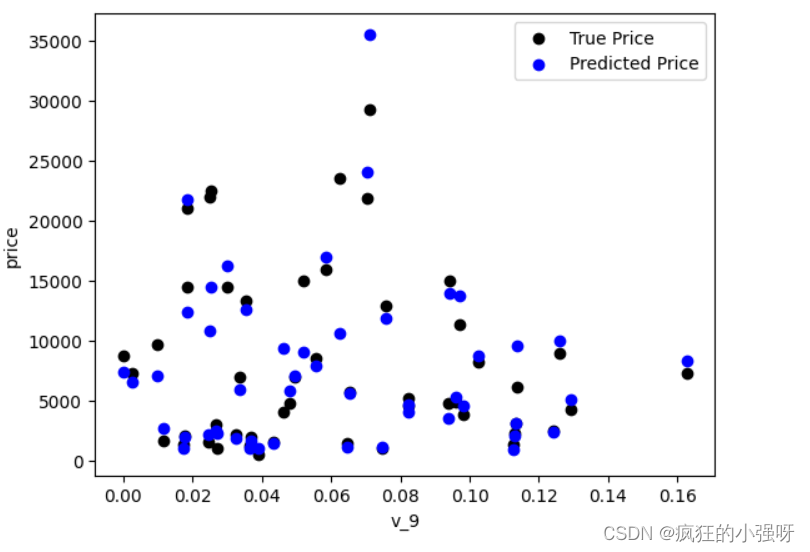
画图查看真实值与预测值之间的差距:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt subsample_index = np.random.randint(low=0, high=len(train_y), size=50) # 从训练数据中随机选择 50 个样本的索引 plt.scatter(train_X['v_9'][subsample_index], train_y[subsample_index], color='black') # 绘制真实价格与特征 'v_9' 之间的散点图 plt.scatter(train_X['v_9'][subsample_index], model.predict(train_X.loc[subsample_index]), color='blue') # 绘制模型预测价格与特征 'v_9' 之间的散点图 plt.xlabel('v_9') plt.ylabel('price') plt.legend(['True Price','Predicted Price'],loc='upper right') print('The predicted price is obvious different from true price') plt.show()通过作图我们发现数据的标签(price)呈现长尾分布,不利于我们的建模预测。
对标签进行进一步分析:
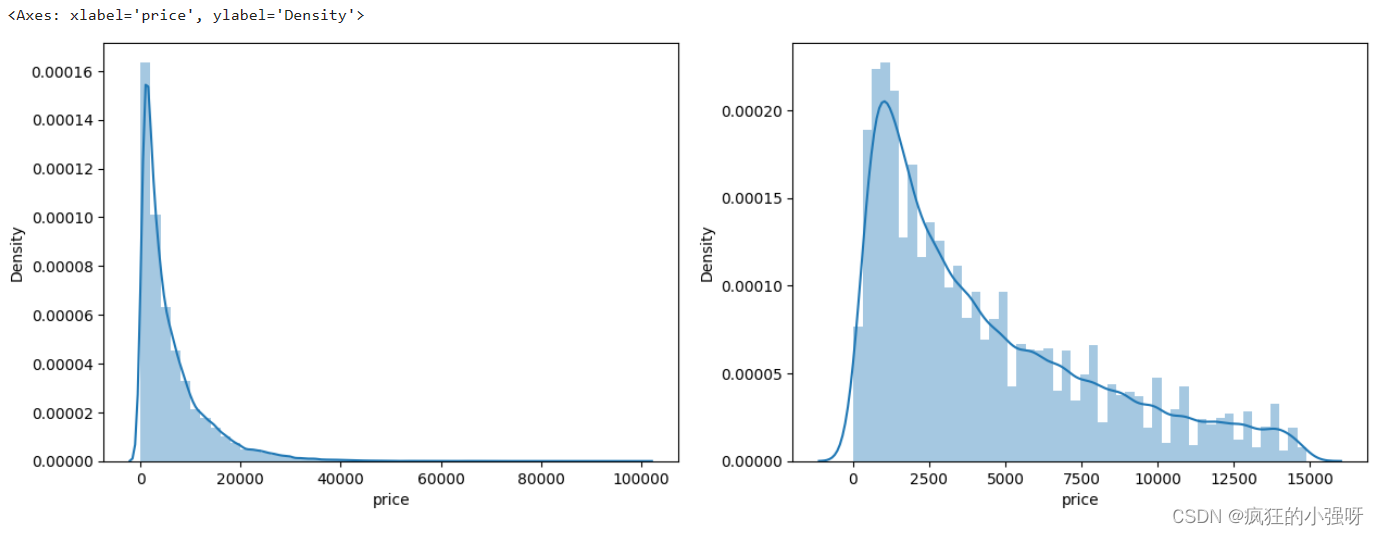
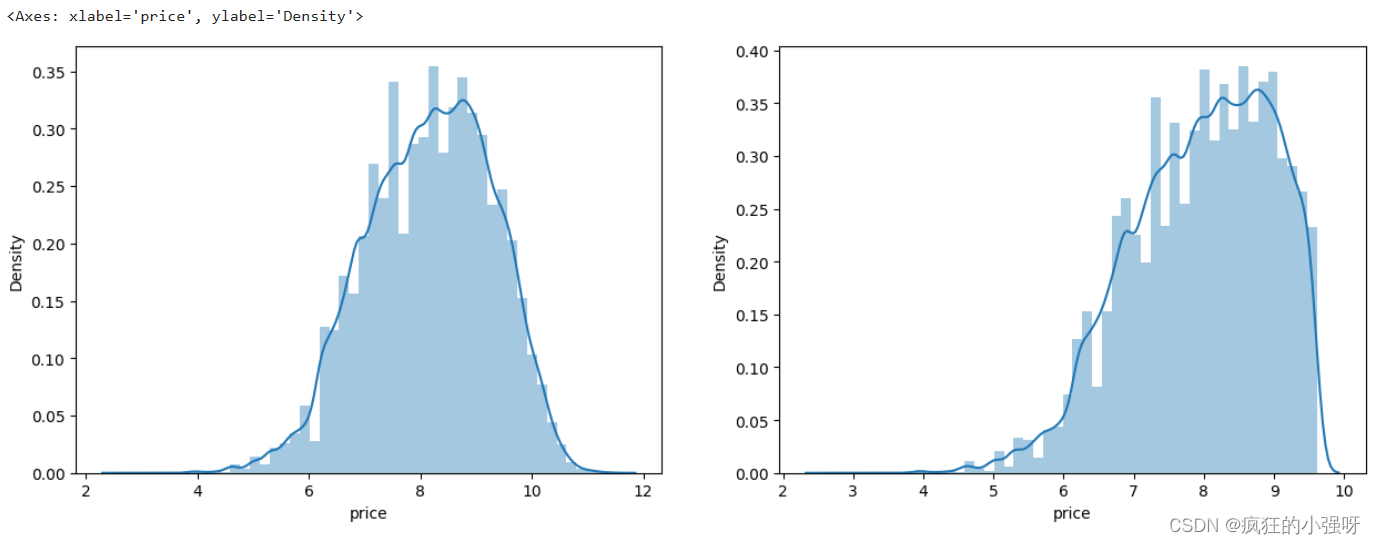
画图显示标签的分布:左边是所有标签数据的一个分布,右边是去掉最大的10%标签数据之后的一个分布
import seaborn as sns print('It is clear to see the price shows a typical exponential distribution') plt.figure(figsize=(15,5)) plt.subplot(1,2,1) # 创建一个包含 1 行 2 列的子图,并将当前子图设置为第一个子图 sns.distplot(train_y) # 显示价格数据的直方图以及拟合的密度曲线 plt.subplot(1,2,2) # quantile 函数来计算价格数据的第 90%分位数,然后通过布尔索引选取低于第 90 百分位数的价格数据 sns.distplot(train_y[train_y对标签进行 log(x+1) 变换,使标签贴近于正态分布:
train_y_ln = np.log(train_y + 1)
显示log变化之后的数据分布:
import seaborn as sns print('The transformed price seems like normal distribution') plt.figure(figsize=(15,5)) plt.subplot(1,2,1) sns.distplot(train_y_ln) plt.subplot(1,2,2) sns.distplot(train_y_ln[train_y_ln然后我们重新训练,再可视化
model = model.fit(train_X, train_y_ln) print('intercept:'+ str(model.intercept_)) sorted(dict(zip(continuous_feature_names, model.coef_)).items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True) plt.scatter(train_X['v_9'][subsample_index], train_y[subsample_index], color='black') plt.scatter(train_X['v_9'][subsample_index], np.exp(model.predict(train_X.loc[subsample_index])), color='blue') plt.xlabel('v_9') plt.ylabel('price') plt.legend(['True Price','Predicted Price'],loc='upper right') print('The predicted price seems normal after np.log transforming') plt.show()可以看出结果要比上面的好一点:
3. 五折交叉验证
在使用训练集对参数进行训练的时候,一般会将整个训练集分为三个部分:训练集(train_set),评估集(valid_set),测试集(test_set)这三个部分。这其实是为了保证训练效果而特意设置的。
- 测试集很好理解,其实就是完全不参与训练的数据,仅仅用来观测测试效果的数据。
- 在实际的训练中,训练的结果对于训练集的拟合程度通常还是挺好的(初始条件敏感),但是对于训练集之外的数据的拟合程度通常就不那么令人满意了。因此我们通常并不会把所有的数据集都拿来训练,而是分出一部分来(这一部分不参加训练)对训练集生成的参数进行测试,相对客观的判断这些参数对训练集之外的数据的符合程度。这种思想就称为交叉验证(Cross Validation)
(1)使用线性回归模型,对未处理标签的特征数据进行五折交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error, make_scorer # 下面这个函数主要实现对参数进行对数转换输入目标函数 def log_transfer(func): def wrapper(y, yhat): # np.nan_to_num 函数用于将对数转换后可能出现的 NaN 值转换为 0 result = func(np.log(y), np.nan_to_num(np.log(yhat))) return result # 返回内部函数 wrapper,这是一个对原始函数的包装器,它将对传入的参数进行对数转换后再调用原始函数 return wrapper # 计算5折交叉验证得分 scores = cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y, verbose=1, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(log_transfer(mean_absolute_error))) # model 是要评估的模型对象。 # train_X 是训练数据的特征,train_y 是训练数据的目标变量。 # verbose=1 设置为 1 时表示打印详细信息。 # cv=5 表示进行 5 折交叉验证。 # scoring=make_scorer(log_transfer(mean_absolute_error)) 指定了评分标准 # 使用了 make_scorer 函数将一个自定义的评分函数 log_transfer(mean_absolute_error) 转换为一个可用于评分的评估器。 # log_transfer(mean_absolute_error) 这一步的作用就是将真实值和预测值在输入到mean_absolute_error之前进行log转换 # mean_absolute_error 是一个回归问题中常用的评估指标,用于衡量预测值与实际值之间的平均绝对误差 print('AVG:', np.mean(scores))结果展示:
使用线性回归模型,对处理过标签的特征数据进行五折交叉验证:
scores = cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=1, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)) print('AVG:', np.mean(scores))结果展示:
可以看见,调整之后的数据,误差明显变小
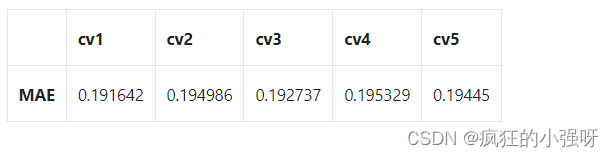
查看scores:
scores = pd.DataFrame(scores.reshape(1,-1)) scores.columns = ['cv' + str(x) for x in range(1, 6)] scores.index = ['MAE'] scores
4. 模拟真实业务情况
交叉验证在某些与时间相关的数据集上可能反映了不真实的情况,比如我们不能通过2018年的二手车价格来预测2017年的二手车价格。这个时候我们可以采用时间顺序对数据集进行分隔。在本例中,我们可以选用靠前时间的4/5样本当作训练集,靠后时间的1/5当作验证集
具体操作如下:
import datetime sample_feature = sample_feature.reset_index(drop=True) split_point = len(sample_feature) // 5 * 4 train = sample_feature.loc[:split_point].dropna() val = sample_feature.loc[split_point:].dropna() train_X = train.drop('price',axis=1) train_y_ln = np.log(train['price'] + 1) val_X = val.drop('price',axis=1) val_y_ln = np.log(val['price'] + 1) model = model.fit(train_X, train_y_ln) mean_absolute_error(val_y_ln, model.predict(val_X))结果展示:
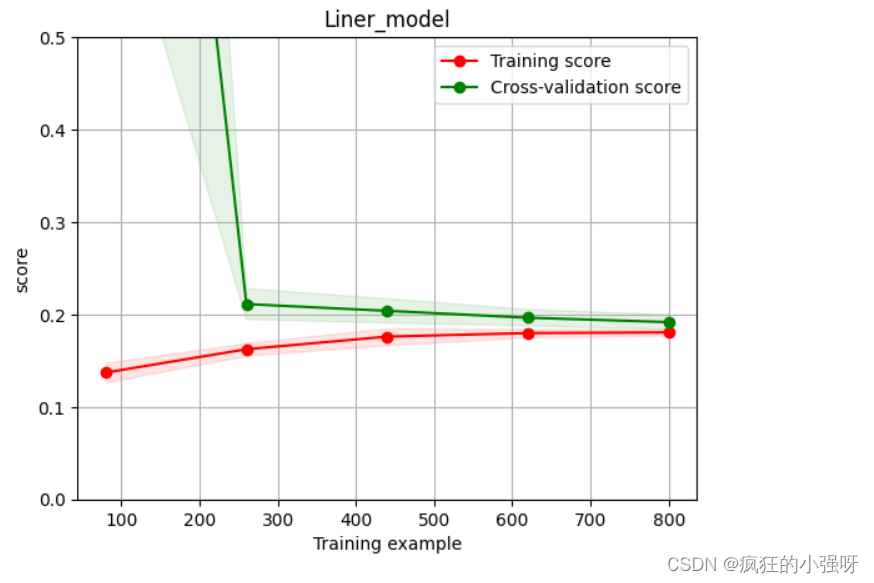
5. 绘制学习率曲线与验证曲线
def plot_learning_curve(estimator, title, X, y, ylim=None, cv=None,n_jobs=1, train_size=np.linspace(.1, 1.0, 5 )): """ 模型估计器 estimator 图的标题 title 特征数据 X 目标数据 y y轴的范围 ylim 交叉验证分割策略 cv 并行运行的作业数 n_jobs 训练样本的大小 train_size """ plt.figure() plt.title(title) if ylim is not None: plt.ylim(*ylim) # 设置 y 轴的范围为 ylim plt.xlabel('Training example') plt.ylabel('score') # 使用 learning_curve 函数计算学习曲线的训练集得分和交叉验证集得分 train_sizes, train_scores, test_scores = learning_curve(estimator, X, y, cv=cv, n_jobs=n_jobs, train_sizes=train_size, scoring = make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)) train_scores_mean = np.mean(train_scores, axis=1) # 计算训练集得分的均值 train_scores_std = np.std(train_scores, axis=1) # 计算训练集得分的标准差 test_scores_mean = np.mean(test_scores, axis=1) test_scores_std = np.std(test_scores, axis=1) plt.grid()#区域 # 使用红色填充训练集得分的方差范围 plt.fill_between(train_sizes, train_scores_mean - train_scores_std, train_scores_mean + train_scores_std, alpha=0.1, color="r") # 使用绿色填充交叉验证集得分的方差范围 plt.fill_between(train_sizes, test_scores_mean - test_scores_std, test_scores_mean + test_scores_std, alpha=0.1, color="g") # 绘制训练集得分曲线 plt.plot(train_sizes, train_scores_mean, 'o-', color='r', label="Training score") # 绘制交叉验证集得分曲线 plt.plot(train_sizes, test_scores_mean,'o-',color="g", label="Cross-validation score") plt.legend(loc="best") return plt plot_learning_curve(LinearRegression(), 'Liner_model', train_X[:1000], train_y_ln[:1000], ylim=(0.0, 0.5), cv=5, n_jobs=1)6. 嵌入式特征选择
在过滤式和包裹式特征选择方法中,特征选择过程与学习器训练过程有明显的分别。而嵌入式特征选择在学习器训练过程中自动地进行特征选择。嵌入式选择最常用的是L1正则化与L2正则化。在对线性回归模型加入两种正则化方法后,他们分别变成了岭回归与Lasso回归
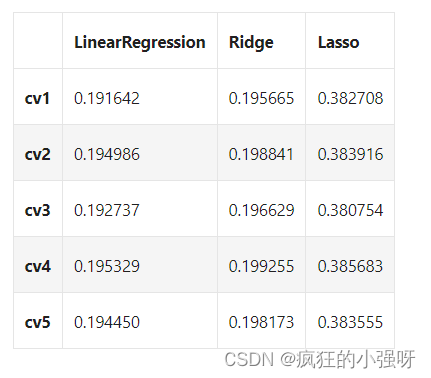
对上述三种模型进行交叉验证训练,并对比结果:
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso # 创建一个模型实力列表 models = [LinearRegression(), Ridge(), Lasso()] result = dict() for model in models: model_name = str(model)[:-2] # 获取模型名称 # 训练模型 scores = cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)) # 收集各模型训练得分 result[model_name] = scores print(model_name + ' is finished') result = pd.DataFrame(result) result.index = ['cv' + str(x) for x in range(1, 6)] result结果展示:
分别对三个模型训练得到的参数进行分析:
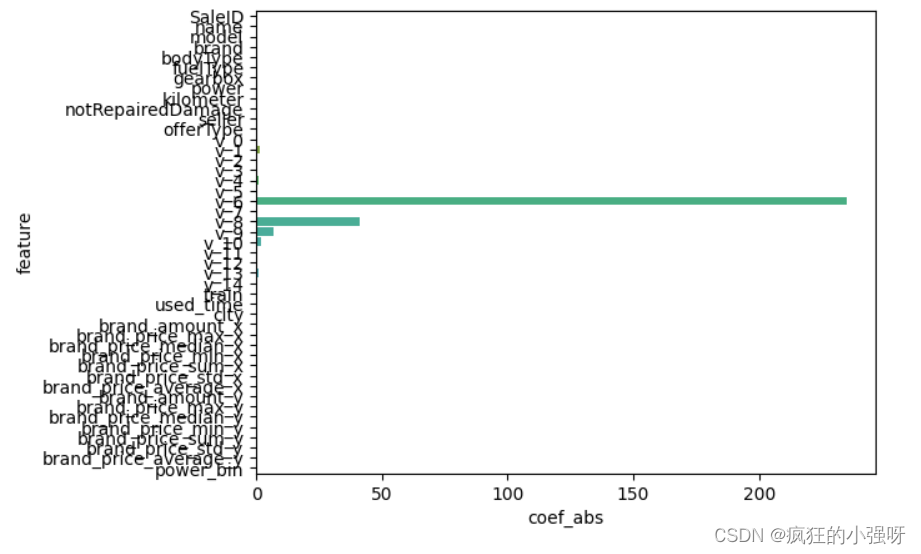
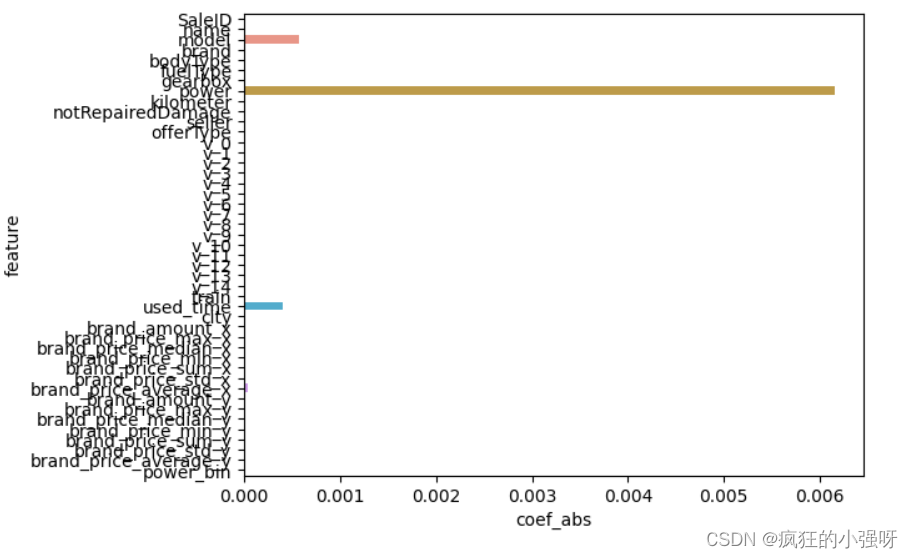
- 一般线性回归
import seaborn as sns model = LinearRegression().fit(train_X, train_y_ln) print('intercept:', model.intercept_) # 组合数据 data = pd.DataFrame({'coef_abs': abs(model.coef_), 'feature': train_X.columns}) # 画图 sns.barplot(x='coef_abs', y='feature', data=data)展示:
- 岭回归
L2正则化在拟合过程中通常都倾向于让权值尽可能小,最后构造一个所有参数都比较小的模型。因为一般认为参数值小的模型比较简单,能适应不同的数据集,也在一定程度上避免了过拟合现象。可以设想一下对于一个线性回归方程,若参数很大,那么只要数据偏移一点点,就会对结果造成很大的影响;但如果参数足够小,数据偏移得多一点也不会对结果造成什么影响,专业一点的说法是『抗扰动能力强』
import seaborn as sns model = Ridge().fit(train_X, train_y_ln) print('intercept:', model.intercept_) # 组合数据 data = pd.DataFrame({'coef_abs': abs(model.coef_), 'feature': train_X.columns}) sns.barplot(x='coef_abs', y='feature', data=data)展示:
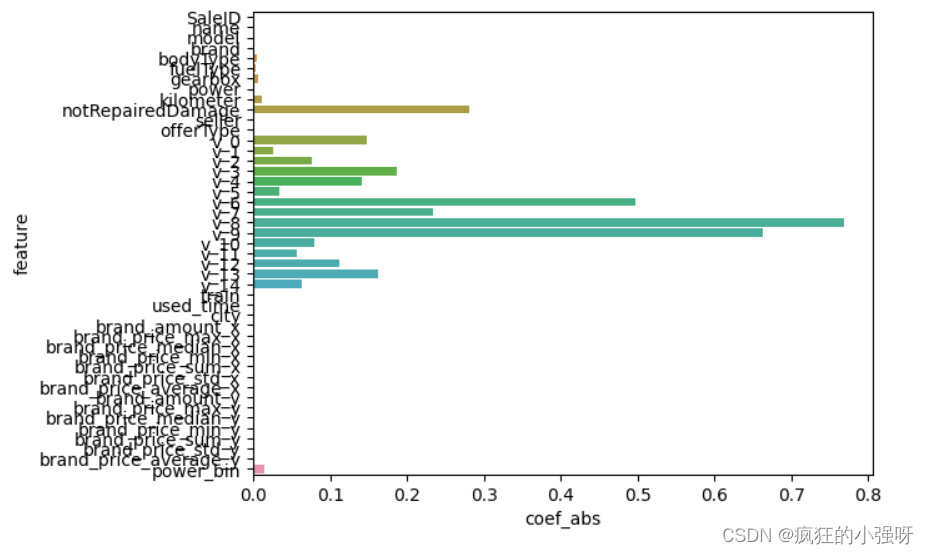
- Lasso回归
L1正则化有助于生成一个稀疏权值矩阵,进而可以用于特征选择
import seaborn as sns model = Lasso().fit(train_X, train_y_ln) print('intercept:', model.intercept_) # 组合数据 data = pd.DataFrame({'coef_abs': abs(model.coef_), 'feature': train_X.columns}) sns.barplot(x='coef_abs', y='feature', data=data)展示:
在这里我们可以看到power、used_time等特征非常重要
6. 非线性模型
决策树通过信息熵或GINI指数选择分裂节点时,优先选择的分裂特征也更加重要,这同样是一种特征选择的方法。XGBoost与LightGBM模型中的model_importance指标正是基于此计算的
下面我们选择部分模型进行对比:
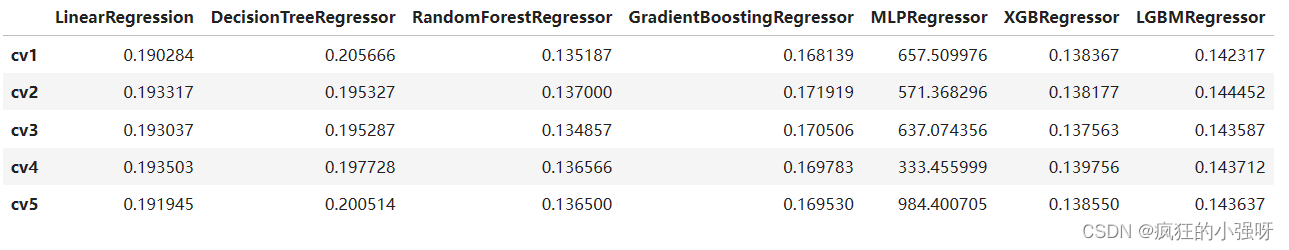
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor from xgboost.sklearn import XGBRegressor from lightgbm.sklearn import LGBMRegressor models = [LinearRegression(), DecisionTreeRegressor(), RandomForestRegressor(), GradientBoostingRegressor(), MLPRegressor(solver='lbfgs', max_iter=100), XGBRegressor(n_estimators = 100, objective='reg:squarederror'), LGBMRegressor(n_estimators = 100)] result = dict() for model in models: model_name = str(model).split('(')[0] scores = cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)) result[model_name] = scores print(model_name + ' is finished') result = pd.DataFrame(result) result.index = ['cv' + str(x) for x in range(1, 6)] result结果:
可以看到随机森林模型在每一个fold中均取得了更好的效果!!!
7. 模型调参
在这里主要介绍三种调参方法
(1) 贪心调参
所谓贪心算法是指,在对问题求解时,总是做出在当前看来是最好的选择。也就是说,不从整体最优上加以考虑,它所做出的仅仅是在某种意义上的局部最优解。
以lightgbm模型为例:
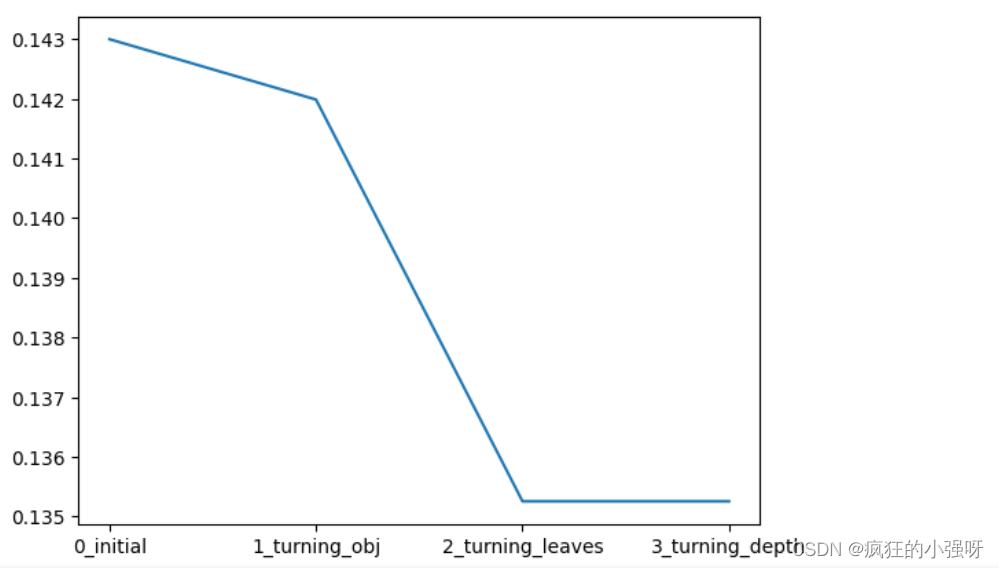
## LGB的参数集合: # 损失函数 objective = ['regression', 'regression_l1', 'mape', 'huber', 'fair'] # 叶子节点数 num_leaves = [3,5,10,15,20,40, 55] # 最大深度 max_depth = [3,5,10,15,20,40, 55] bagging_fraction = [] feature_fraction = [] drop_rate = [] best_obj = dict() # 计算不同选择下对应结果,其中 score最小时为最优结果 for obj in objective: model = LGBMRegressor(objective=obj) score = np.mean(cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error))) best_obj[obj] = score best_leaves = dict() for leaves in num_leaves: model = LGBMRegressor(objective=min(best_obj.items(), key=lambda x:x[1])[0], num_leaves=leaves) score = np.mean(cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error))) best_leaves[leaves] = score best_depth = dict() for depth in max_depth: model = LGBMRegressor(objective=min(best_obj.items(), key=lambda x:x[1])[0], num_leaves=min(best_leaves.items(), key=lambda x:x[1])[0], max_depth=depth) score = np.mean(cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error))) best_depth[depth] = score # 画出各选择下,损失的变化 sns.lineplot(x=['0_initial','1_turning_obj','2_turning_leaves','3_turning_depth'], y=[0.143 ,min(best_obj.values()), min(best_leaves.values()), min(best_depth.values())])(2)Grid Search 调参
GridSearchCV:一种调参的方法,当你算法模型效果不是很好时,可以通过该方法来调整参数,通过循环遍历,尝试每一种参数组合,返回最好的得分值的参数组合
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV parameters = {'objective': objective , 'num_leaves': num_leaves, 'max_depth': max_depth} model = LGBMRegressor() clf = GridSearchCV(model, parameters, cv=5) clf = clf.fit(train_X, train_y_ln) clf.best_params_得到的最佳参数为:{'max_depth': 10, 'num_leaves': 55, 'objective': 'huber'}
我们再用最佳参数来训练模型:
model = LGBMRegressor(objective='huber', num_leaves=55, max_depth=10) np.mean(cross_val_score(model, X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error)))结果跟之前的调参是相当的:
(3)贝叶斯调参
贝叶斯优化通过基于目标函数的过去评估结果建立替代函数(概率模型),来找到最小化目标函数的值。贝叶斯方法与随机或网格搜索的不同之处在于,它在尝试下一组超参数时,会参考之前的评估结果,因此可以省去很多无用功。
from bayes_opt import BayesianOptimization def rf_cv(num_leaves, max_depth, subsample, min_child_samples): #num_leaves: 决策树上的叶子节点数量。较大的值可以提高模型的复杂度,但也容易导致过拟合。 # max_depth: 决策树的最大深度。控制树的深度可以限制模型的复杂度,有助于防止过拟合。 # subsample: 训练数据的子样本比例。该参数可以用来控制每次迭代时使用的数据量,有助于加速训练过程并提高模型的泛化能力。 # min_child_samples: 每个叶子节点所需的最小样本数。通过限制叶子节点中的样本数量,可以控制树的生长,避免过拟合。 val = cross_val_score( LGBMRegressor(objective = 'regression_l1', num_leaves=int(num_leaves), max_depth=int(max_depth), subsample = subsample, min_child_samples = int(min_child_samples) ), X=train_X, y=train_y_ln, verbose=0, cv = 5, scoring=make_scorer(mean_absolute_error) ).mean() return 1 - val rf_bo = BayesianOptimization( rf_cv, { 'num_leaves': (2, 100), 'max_depth': (2, 100), 'subsample': (0.1, 1), 'min_child_samples' : (2, 100) } ) # 最大化 rf_cv 函数返回的值,即最小化负的平均绝对误差 rf_bo.maximize()结果:
1 - rf_bo.max['target']
总结
- 上述我们主要通过log转换、正则化、模型选择、参数微调等方法来提高预测的精度
- 最后附上一些学习链接供大家参考:
- 线性回归模型:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49480391
- 决策树模型:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/65304798
- GBDT模型:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/45145899
- XGBoost模型:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/86816771
- LightGBM模型:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/89360721
- 用简单易懂的语言描述「过拟合 overfitting」?https://www.zhihu.com/question/32246256/answer/55320482
- 模型复杂度与模型的泛化能力:http://yangyingming.com/article/434/
- 正则化的直观理解:https://blog.csdn.net/jinping_shi/article/details/52433975
- 贪心算法: https://www.jianshu.com/p/ab89df9759c8
- 网格调参: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43172660/article/details/83032029
- 贝叶斯调参: https://blog.csdn.net/linxid/article/details/81189154
- Lasso回归
- 岭回归
- 一般线性回归



.png)