【C++】类的默认成员函数
类的默认成员函数
- 类的六个默认成员函数
- 构造函数
- 构造函数的概念
- 构造函数的特性
- 析构函数
- 析构函数的概念
- 析构函数的特性
- 构造函数与析构函数的调用顺序
- 拷贝构造
- 拷贝构造的概念
- 拷贝构造的特性
- 赋值运算符重载
- 运算符重载
- 赋值运算符重载
- 前置++与后置++重载
- 输入输出流重载
- const修饰成员
- 实现完整的日期系统
- 取地址操作符重载
- const取地址操作符重载
类的六个默认成员函数
当一个类中什么成员都没有时被称为空类。
空类:即任何类在什么都不写时,编译器会自动生成6个默认成员函数。
默认成员函数:用户没有显式实现,编译器会自动生成的成员函数称为默认成员函数。
构造函数
构造函数的概念
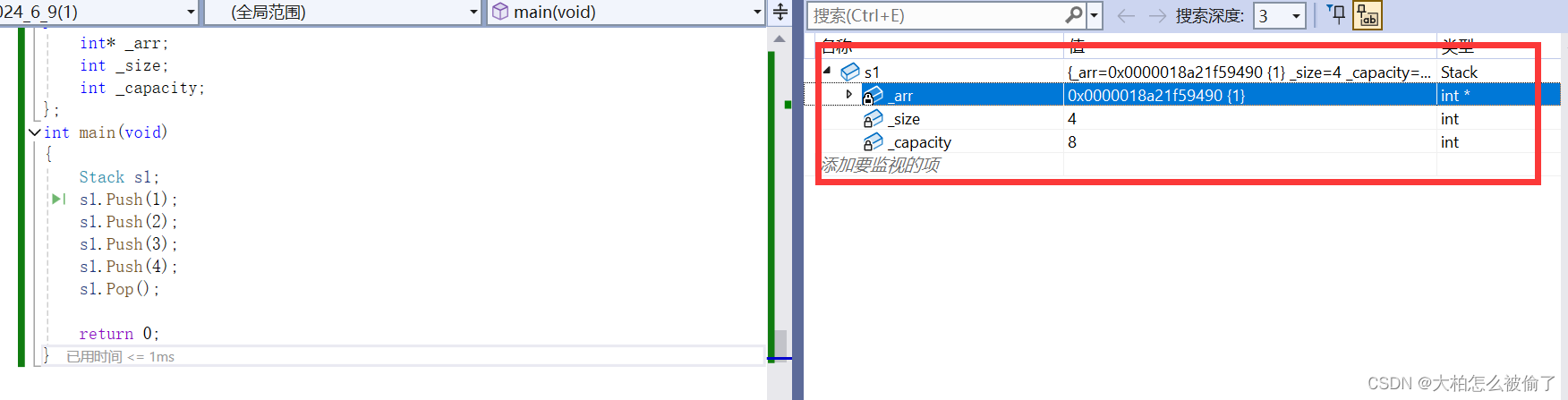
class Data { public: void Init(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } void Print() { cout Data d1; d1.Init(); d1.Print(); Data d2; d2.Init(2024,6,8); d2.Print(); return 0; } public: Data(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main(void) { Data d1(); return 0; } public: //带参数的构造函数 Data(int year, int month, int day) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } //不带参数的构造函数 Data() { _year = 2000; _month = 1; _day = 1; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main(void) { //调用带参数的构造函数 Data d1(2024,6,8); //调用不带参数的构造函数 Data d2; return 0; } public: void Print() { cout Data d1; d1.Print(); return 0; } public: void Print() { cout public: //无参构造函数 Data() { _year = 2000; _month = 1; _day = 1; } //全参构造函数 Data(int year = 2000,int month = 1, int day = 1) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main(void) { Data d1; return 0; } public: Data(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1) { this-_year = year; this-_month = month; this-_day = day; } ~Data() { _year = 0; _month = 0; _day = 0; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; public: Data(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1) { cout cout Data d1; return 0; } public: Stack(int capacity = 4) { _arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * capacity); if (_arr == nullptr) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } _capacity = capacity; _size = 1; } ~Stack() { free(_arr); _arr = nullptr; _size = 1; _capacity = 0; } void Push(int x) { if (this-_capacity == this-_size) { int* arr = (int*)realloc(this-_arr, sizeof(int) * this-_capacity * 2); if (arr == nullptr) { perror("realloc fail"); return; } this-_arr = arr; this-_capacity *= 2; } this-_arr[this-_size - 1] = x; this-_size++; } void Pop() { this-_arr[this-_size - 1] = 0; this-_size--; } private: int* _arr; int _size; int _capacity; }; int main(void) { Stack s1; s1.Push(1); s1.Push(2); s1.Push(3); s1.Push(4); s1.Pop(); return 0; } public: Stack(int capacity = 4) { _arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * capacity); if (_arr == nullptr) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } _capacity = capacity; _size = 1; } void Push(int x) { if (this-_capacity == this-_size) { int* arr = (int*)realloc(this-_arr, sizeof(int) * this-_capacity * 2); if (arr == nullptr) { perror("realloc fail"); return; } this->_arr = arr; this->_capacity *= 2; } this->_arr[this->_size - 1] = x; this->_size++; } void Pop() { this->_arr[this->_size - 1] = 0; this->_size--; } private: int* _arr; int _size; int _capacity; }; int main(void) { Stack s1; s1.Push(1); s1.Push(2); s1.Push(3); s1.Push(4); s1.Pop(); return 0; }所以,一般情况下如果没有动态内存申请,析构函数可以不写,例如:Data类;但是如果有动态内存申请,就需要显式写析构函数释放资源,否则会造成内存泄漏。例如:栈的实现。
构造函数与析构函数的调用顺序
-
类的析构函数调用一般按照构造函数调用的相反顺序调用,但是需要注意static对象的存在,因为static改变了对象的生存作用域,需要等待程序结束后才可析构释放对象。
-
全局对象先于局部对象进行构造。
-
局部对象按照顺序进行构造,无论是否为static对象。
-
static修饰的对象会在局部对象析构后进行析构。
拷贝构造
拷贝构造的概念
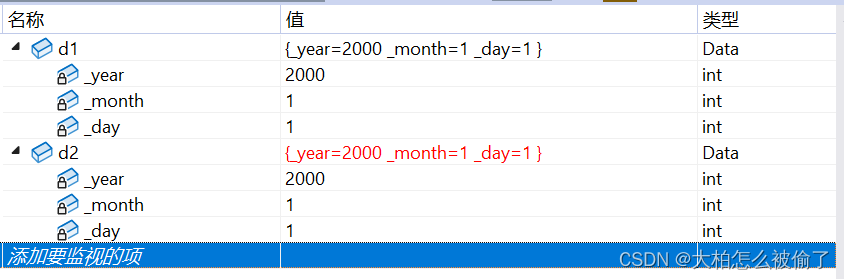
创建对象时,需要创建一个与已存在对象一模一样的新对象,就需要用到拷贝构造。
拷贝构造:只有单个形参,该形参是对本类型对象的引用(一般常用const修饰),在用已存在的类型对象创建新对象时由编译器自动调用。
拷贝构造的特性
拷贝构造函数也是特殊的成员函数,其特征如下:
1.拷贝构造函数时构造函数的一个重载形式,所有书写格式与构造函数类似,但是参数类型不同。
2.拷贝构造函数的参数只有一个且必须是类类型对象的引用,使用传值方式编译器之间报错,因为会引发无穷递归调用。
观察下面代码:
class Data { public: Data(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1) { cout _month = month; this->_day = day; } ~Data() { cout _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main(void) { Data d1; Data d2(d1); return 0; } public: Data(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1) { this-_year = year; this-_month = month; this->_day = day; } ~Data() { _year = 0; _month = 0; _day = 0; } //拷贝构造函数 //传值 Data(const Data& d) { _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main(void) { Data d1; Data d2(d1); return 0; }3.如果没有显式定义,编译器会生成默认的拷贝构造函数,默认的拷贝构造函数对象按内存存储按字节序完成拷贝,这种拷贝叫浅拷贝,或者值拷贝。
(1)内置类型成员完成值拷贝、浅拷贝。
(2)自定义类型成员会调用他的拷贝构造。
观察代码:
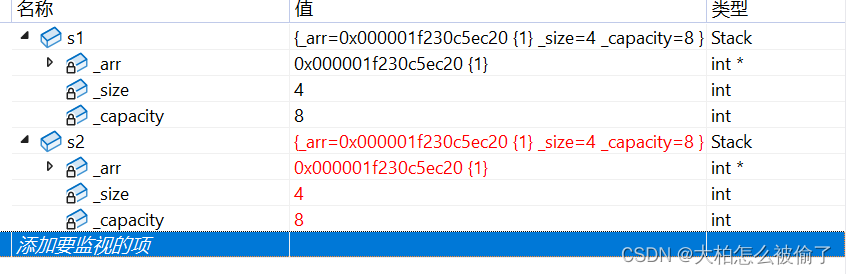
class Stack { public: Stack(int capacity = 4) { _arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * capacity); if (_arr == nullptr) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } _capacity = capacity; _size = 1; } void Push(int x) { if (this->_capacity == this->_size) { int* arr = (int*)realloc(this->_arr, sizeof(int) * this->_capacity * 2); if (arr == nullptr) { perror("realloc fail"); return; } this->_arr = arr; this->_capacity *= 2; } this->_arr[this->_size - 1] = x; this->_size++; } void Pop() { this->_arr[this->_size - 1] = 0; this->_size--; } private: int* _arr; int _size; int _capacity; }; int main(void) { Stack s1; s1.Push(1); s1.Push(2); s1.Push(3); s1.Push(4); s1.Pop(); Stack s2(s1); return 0; }以栈为例,栈不可以使用默认拷贝构造,栈默认生成的拷贝构造会将俩个指针指向同一个栈,在析构时,后面拷贝的指针会先析构,而前面被拷贝的指针会后析构,一个堆区被析构俩次,编译器会报错,同时如果修改其中一个值,会影响另一个。
栈拷贝构造的正确代码是:
Stack(const Stack& s) { _arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * s._capacity); if (_arr == nullptr) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } memcpy(_arr, s._arr, sizeof(int) * s._size); _size = s._size; _capacity = s._capacity; }需要动态开辟的都需要自己实现深拷贝,而像日期类可以不写拷贝构造,默认生成的拷贝构造就可以用。
赋值运算符重载
运算符重载
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通函数类似。
函数名字为:关键字operator后面接需要重载的运算符符号。
函数原型:返回值类型 operator操作符(参数列表)
- 内置类型可以通过编译器计算,而自定义类型也可以向内置类型一样,需要通过运算符重载,进行加、减、比较等。
以Date日期类举例:是否使用重载运算符,是观察这个运算符对这个类是否有意义,例如:日期相减可以计算相差天数,而日期相加却没有意义。
下面演示日期比较大小:
class Date { public: //Date构造 Date(int year = 2000,int month = 1, int day = 1) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } //Date默认析构,默认拷贝 // //private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; bool operator>(const Date& d1, const Date& d2) { if (d1._year > d2._year) { return true; } else if (d1._year == d2._year && d1._month > d2._month) { return true; } else if (d1._year == d2._year && d1._month == d2._month && d1._day > d2._day) { return true; } return false; } int main(void) { Date d1(2024, 6, 10); Date d2(2024, 5, 20); if (d1 > d2) { cout cout (d1,d1)是相同的,第二种方式相当于调用函数。int main(void) { Date d1(2024, 6, 10); Date d2(2024, 5, 20); //第一种方式 if (d1 > d2) { cout cout cout cout public: //Date构造 Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } //Date默认析构,默认拷贝 //比较大小的运算符重载 bool operator(const Date& d) { if (_year d._year) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year && _month d._month) { return true; } else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day d._day) { return true; } return false; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main(void) { Date d1(2024, 6, 10); Date d2(2024, 5, 20); //第一种方式 if (d1 d2) { cout cout cout cout _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; } //调用拷贝构造函数 Date d1(2024, 6, 10); Date d2 = d1; //调用运算符重载函数 Date d3(2024, 5, 20); Date d4(2003, 2, 3); d3 = d4; return 0; } _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; return *this; } _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; return *this; } if (this != &d) { _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; } return *this; } _day = _day + 1; return *this; } Date tmp(*this); _day = _day + 1; return tmp; } out int i = 10; cout public: //公有的成员函数 int GetYear() { return _year; } int GetMonth() { return _month; } int GetDay() { return _day; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; //全局的流插入操作符 void operator out public: //友元函数声明 friend void operator out out public: //友元函数声明 friend ostream& operator out public: //友元函数声明 friend istream& operator(istream& in, Date& d); private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; //全局的流提取操作符 istream& operator(istream& in, Date& d) { in d._year d._month d._day; return in; } public: //全缺省的构造函数 Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1); //析构函数 ~Date(); //拷贝构造函数 Date(const Date& d); //赋值运算符重载 Date& operator=(const Date& d); //打印 void Print() const { cout if (month 0 && month
- 内置类型可以通过编译器计算,而自定义类型也可以向内置类型一样,需要通过运算符重载,进行加、减、比较等。
-