Python | 海表面温度(SST) | 长期趋势和异常分析
趋势和异常分析(Trend and anomaly)在大气和海洋学研究中被广泛用于探测长期变化。
趋势分析(Trend Analysis):
趋势分析是一种用于检测数据随时间的变化趋势的方法。在海洋学和大气学中,常见的趋势分析包括海表面温度(SST)、海平面上升、气温变化等。趋势分析通常包括以下步骤:
- 数据预处理:首先需要对数据进行预处理,包括去除季节循环、填补缺失值等。
- 计算趋势:采用统计方法(如线性回归、非线性回归)来计算数据随时间的变化趋势。常见的趋势计算方法包括最小二乘法、曲线拟合等。
- 趋势显著性检验:对计算得到的趋势进行显著性检验,以确定趋势是否具有统计显著性。常见的显著性检验方法包括t检验、F检验等。
- 趋势可视化:将计算得到的趋势以图形方式呈现,通常使用折线图或柱状图来展示数据随时间的变化趋势。
趋势分析的结果可以帮助科学家们了解气候系统的长期演变趋势,从而预测未来可能的变化情况。
异常分析(Anomaly Analysis):
异常分析是一种用于检测数据中非正常事件或突发事件的方法。在海洋学和大气学中,异常分析通常用于检测气候系统中的异常事件,如El Niño事件、极端气候事件等。异常分析通常包括以下步骤:
- 基准确定:选择一个合适的基准期,通常是一段相对稳定的时间段,用于计算异常值。
- 计算异常:将观测数据与基准期的平均值进行比较,计算出每个时间点的异常值。异常值表示该时间点的数据与基准期相比的偏离程度。
- 异常检测:对计算得到的异常值进行检测,识别出突发事件或非正常事件。
- 异常可视化:将计算得到的异常值以图形方式呈现,通常使用折线图或柱状图来展示异常事件的发生情况。
异常分析的结果可以帮助科学家们理解气候系统中的非正常事件,从而采取相应的应对措施或预测未来可能发生的异常情况。
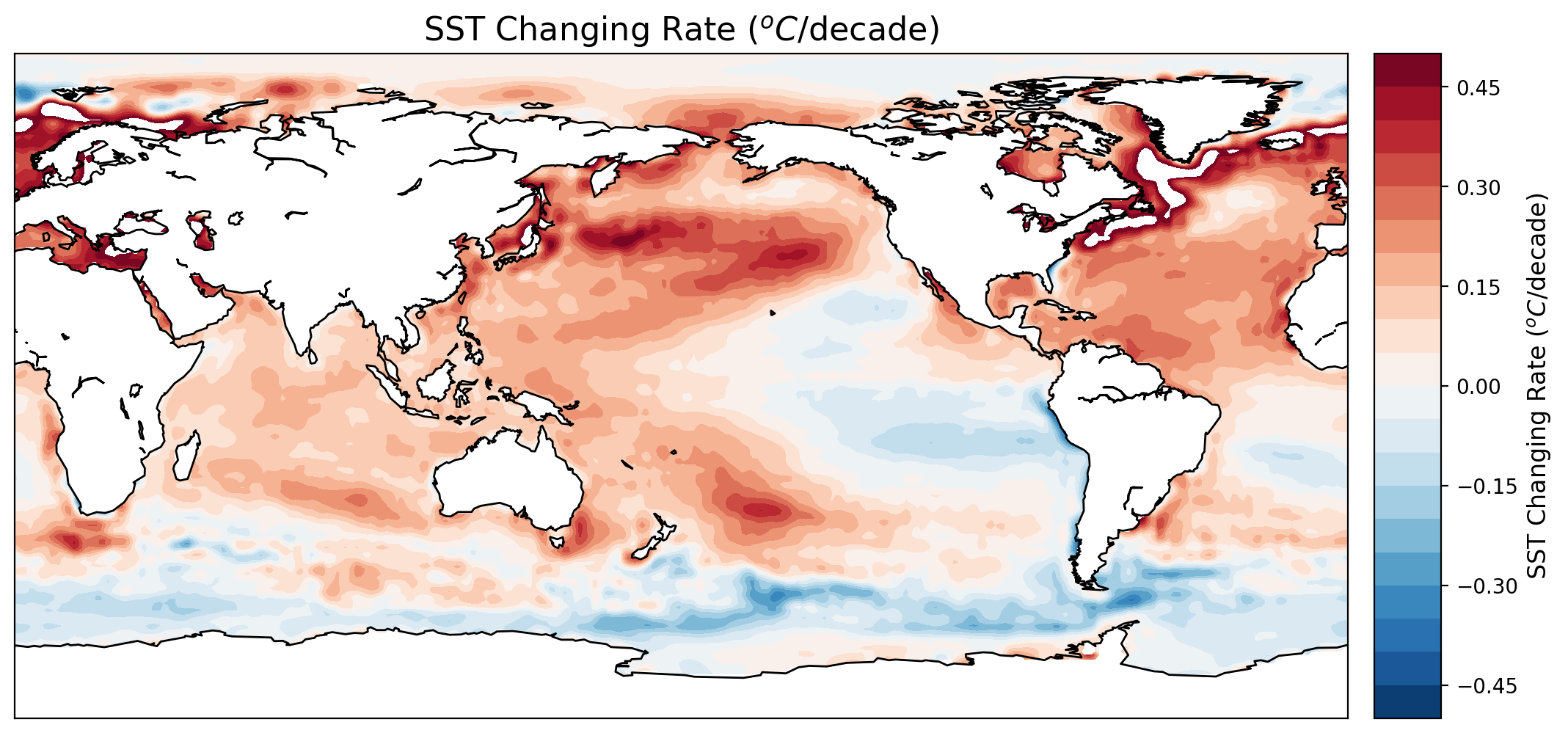
本案例分析以海表温度为例,计算了1982年至2016年全球每十年的温度变化率。此外,还给出了其面积加权的全球月海温异常时间序列。
-
数据来源:
NOAA Optimum Interpolation (OI) Sea Surface Temperature (SST) V2
-
下载地址:
https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/data/gridded/data.noaa.oisst.v2.html
NOAA Optimum Interpolation (OI) Sea Surface Temperature (SST) V2
- 空间分辨率:
1.0纬度 x 1.0经度全球网格(180x360)。
- 覆盖范围
89.5 N-89.5 S 0.5 E-359.5 E.
因为oisst是一个插值数据,所以它覆盖了海洋和陆地。
因此,必须同时使用陆地-海洋掩膜数据,可以从如下网站获得:
https://psl.noaa.gov/repository/entry/show?entryid=b5492d1c-7d9c-47f7-b058-e84030622bbd
1. 加载基础库
import numpy as np import datetime import cftime from netCDF4 import Dataset as netcdf # netcdf4-python module import netCDF4 as nc import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap import matplotlib.dates as mdates from matplotlib.dates import MonthLocator, WeekdayLocator, DateFormatter import matplotlib.ticker as ticker from matplotlib.pylab import rcParams rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 15, 6 import warnings warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # Your code continues here # ================================================================================================ # Author: %(Jianpu)s | Affiliation: Hohai # Email : %(email)s # Last modified: 2024-04-04 12:28:06 # Filename: Trend and Anomaly Analyses.py # Description: # =================================================================================================2. 读取数据、提取变量
2.1 Read SST
ncset= netcdf(r'G:/code_daily/sst.mnmean.nc') lons = ncset['lon'][:] lats = ncset['lat'][:] sst = ncset['sst'][1:421,:,:] # 1982-2016 to make it divisible by 12 nctime = ncset['time'][1:421] t_unit = ncset['time'].units try : t_cal =ncset['time'].calendar except AttributeError : # Attribute doesn't exist t_cal = u"gregorian" # or standard nt, nlat, nlon = sst.shape ngrd = nlon*nlat2.2 解析时间
datevar = nc.num2date(nctime,units = "days since 1800-1-1 00:00:00") print(datevar.shape) datevar[0:5]
2.3读取 mask (1=ocen, 0=land)
lmfile = 'G:/code_daily/lsmask.nc' lmset = netcdf(lmfile) lsmask = lmset['mask'][0,:,:] lsmask = lsmask-1 num_repeats = nt lsm = np.stack([lsmask]*num_repeats,axis=-1).transpose((2,0,1)) lsm.shape
2.3 将海温的陆地区域进行掩膜
sst = np.ma.masked_array(sst, mask=lsm) 3. Trend Analysis 3.1 计算线性趋势 sst_grd = sst.reshape((nt, ngrd), order='F') x = np.linspace(1,nt,nt)#.reshape((nt,1)) sst_rate = np.empty((ngrd,1)) sst_rate[:,:] = np.nan for i in range(ngrd): y = sst_grd[:,i] if(not np.ma.is_masked(y)): z = np.polyfit(x, y, 1) sst_rate[i,0] = z[0]*120.0 #slope, intercept, r_value, p_value, std_err = stats.linregress(x, sst_grd[:,i]) #sst_rate[i,0] = slope*120.0 sst_rate = sst_rate.reshape((nlat,nlon), order='F')3 绘制趋势空间分布
plt.figure(dpi=200) m = Basemap(projection='cyl', llcrnrlon=min(lons), llcrnrlat=min(lats), urcrnrlon=max(lons), urcrnrlat=max(lats)) x, y = m(*np.meshgrid(lons, lats)) clevs = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, 21) cs = m.contourf(x, y, sst_rate.squeeze(), clevs, cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r) m.drawcoastlines() #m.fillcontinents(color='#000000',lake_color='#99ffff') cb = m.colorbar(cs) cb.set_label('SST Changing Rate ($^oC$/decade)', fontsize=12) plt.title('SST Changing Rate ($^oC$/decade)', fontsize=16)4. Anomaly analysis
4.1 转换数据大小为: (nyear) x (12) x (lat x lon)
sst_grd_ym = sst.reshape((12,round(nt/12), ngrd), order='F').transpose((1,0,2)) sst_grd_ym.shape
4.2 计算季节趋势
sst_grd_clm = np.mean(sst_grd_ym, axis=0) sst_grd_clm.shape
4.3 去除季节趋势
sst_grd_anom = (sst_grd_ym - sst_grd_clm).transpose((1,0,2)).reshape((nt, nlat, nlon), order='F') sst_grd_anom.shape
4.4 计算区域权重
4.4.1 确认经纬度的方向
print(lats[0:12]) print(lons[0:12])
4.4.2 计算随纬度变化的区域权重
lonx, latx = np.meshgrid(lons, lats) weights = np.cos(latx * np.pi / 180.) print(weights.shape)
4.4.3 计算全球、北半球、南半球的有效网格总面积
sst_glb_avg = np.zeros(nt) sst_nh_avg = np.zeros(nt) sst_sh_avg = np.zeros(nt) for it in np.arange(nt): sst_glb_avg[it] = np.ma.average(sst_grd_anom[it, :], weights=weights) sst_nh_avg[it] = np.ma.average(sst_grd_anom[it,0:round(nlat/2),:], weights=weights[0:round(nlat/2),:]) sst_sh_avg[it] = np.ma.average(sst_grd_anom[it,round(nlat/2):nlat,:], weights=weights[round(nlat/2):nlat,:])4.5 转换时间为字符串格式
datestr = [date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') for date in datevar]5. 绘制海温异常时间序列
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1 , figsize=(15,5),dpi=200) ax.plot(datestr[::12], sst_glb_avg[::12], color='b', linewidth=2, label='GLB') ax.plot(datestr[::12], sst_nh_avg[::12], color='r', linewidth=2, label='NH') ax.plot(datestr[::12], sst_sh_avg[::12], color='g', linewidth=2, label='SH') ax.set_xticklabels(datestr[::12], rotation=45) ax.axhline(0, linewidth=1, color='k') ax.legend() ax.set_title('Monthly SST Anomaly Time Series (1982 - 2016)', fontsize=16) ax.set_xlabel('Month/Year ', fontsize=12) ax.set_ylabel('$^oC$', fontsize=12) ax.set_ylim(-0.6, 0.6) fig.set_figheight(9) # rotate and align the tick labels so they look better fig.autofmt_xdate() # use a more precise date string for the x axis locations in the toolbar ax.fmt_xdata = mdates.DateFormatter('%Y')http://unidata.github.io/netcdf4-python/
http://www.scipy.org/
本文由mdnice多平台发布
- 覆盖范围
- 空间分辨率:
-